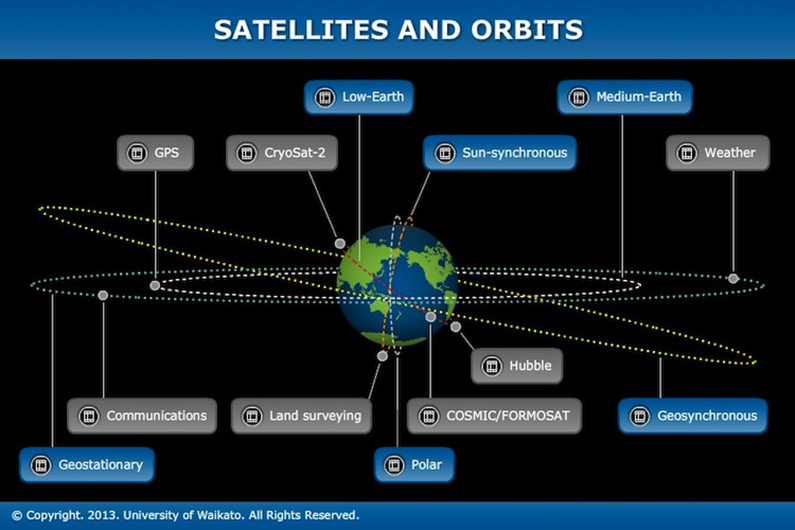
Medium Earth orbit (MEO), sometimes called intermediate circular orbit (ICO), is the region of space around Earth above low Earth orbit (altitude of 2,000 km (1,243 mi) above sea level) and below geosynchronous orbit (altitude of 35,786 km (22,236 mi) above sea level). Those at medium Earth orbit (between about 2,000 and 35,780 km, or 1,242 and 22,232 miles) move more slowly, allowing for more detailed studies of a region. At geosynchronous orbit, however, the. To-scale diagram of low, medium and high Earth orbits. Medium Earth orbit (MEO), sometimes called intermediate circular orbit (ICO), is the region of space around the Earth above low Earth orbit (altitude of 2,000 kilometres (Template:Convert/pround mi)) and below geostationary orbit (altitude of 35,786 kilometres (Template:Convert/pround mi)). Medium earth orbit (MEO) satellite networks will orbit at distances of about 8000 miles from earth's surface. Signals transmitted from a MEO satellite travel a shorter distance. This translates to improved signal strength at the receiving end. This shows that smaller, more lightweight receiving terminals can be used at the receiving end. MEO – Medium Earth Orbit MEO satellites orbit at a lower altitude than GEO, usually occupying the space between 5,000 and 12,000 km (3,100 – 7,500 miles). Their relative proximity to Earth means they achieve far lower latency than GEO units, making them suitable for high-speed telephone signals and similar missions.
- Low Earth Orbit Satellites
- Medium Earth Orbit Satellite
- Medium Earth Orbits Are Used Primarily For Satellites
- Low Earth Orbit
A medium earth orbit satellite (MEO) is a satellite that orbits the earth in between Low Earth Orbit Satellites (LEO), which orbit the earth at a distance from the earth of about 200-930 miles (321.87-1496.69 km) and those satellites which orbit the earth at geostationary orbit, about 22,300 miles (35,888.71 km) above earth. Each type of satellite can provide a different type of coverage for communications and wireless devices. Like LEOs, these satellites don’t maintain a stationary distance from the earth. This is in contrast to the geostationary orbit, where satellites are always approximately 22,300 miles from the earth.
Low Earth Orbit Satellites
Any satellite that orbits the earth between about 1000-22,000 miles (1609.34- 35,405.57 km) above earth is an MEO. Typically the orbit of a medium earth orbit satellite is about 10,000 miles (16,093.44 km) above earth. In various patterns, these satellites make the trip around earth in anywhere from 2-12 hours, which provides better coverage to wider areas than that provided by LEOs.
Medium Earth Orbit Satellite


Medium Earth Orbits Are Used Primarily For Satellites
In 1962, the first communications satellite, Telstar, was launched. It was a medium earth orbit satellite designed to help facilitate high-speed telephone signals, but scientists soon learned what some of the problematic aspects were of a single MEO in space. It only provided transatlantic telephone signals for 20 minutes of each approximately 2.5 hours orbit. It was apparent that multiple MEOs needed to be used in order to provide continuous coverage.
Since then numerous companies have launched both LEOs and MEOs. You need about two dozen LEOs to provide continuous coverage and fewer MEOs. However, LEOs typically orbit in a circular pattern around the equator. A medium earth orbit satellite may have a variety of different orbits, including elliptical ones and may provide better overall coverage of satellite communications, if enough of them are in place and the orbit is swift. The coverage of earth is called a footprint, and MEOs typically are able to create a larger footprint because of their different orbital patterns, and because they are higher than LEOs.
Low Earth Orbit
Today the medium earth orbit satellite is most commonly used in navigation systems around the world. These include Global Positioning System (GPS), and the Russian Glonass. A proposed MEO navigation system for the European Union called Galileo is expected to begin operations in 2013.
